Introduction
Silicone products have become integral in various industries, offering unique properties and applications. In this article, we delve into the world of various silicone materials, specifically focusing on liquid silicone and traditional solid silicone.We aim to provide valuable insights for decision-making.
Join us as we explore the differences between liquid silicone and solid silicone, and uncover their respective advantages and limitations. Discover which type of silicone best suits your needs in this comprehensive comparative analysis.
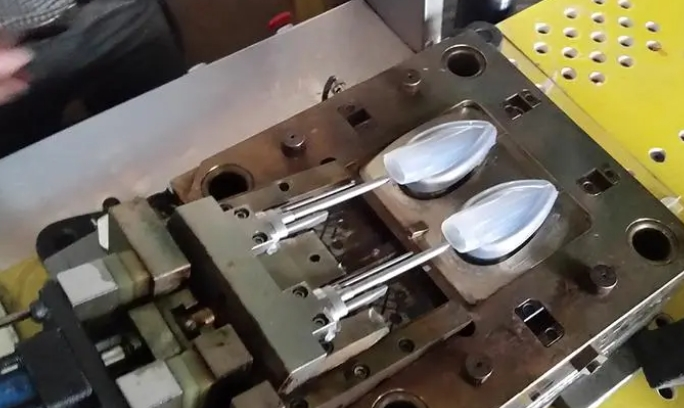

Historical Background
Silicone, a synthetic polymer composed of silicon, oxygen, carbon, and hydrogen, has been a transformative material since its development. Initially used in military and aerospace applications, silicone’s exceptional resistance to extreme temperatures and environmental conditions led to its adoption in various industries.
Over time, silicone’s versatility became evident, making it an essential material in construction, automotive, healthcare, and consumer goods. Its thermal stability, electrical insulation, and chemical inertness contributed to its evolution from a niche material to a widely used substance.
Evolution of Liquid Silicone rubber
Liquid Silicone Rubber (LSR) emerged as a significant advancement in silicone-based materials. Developed in the latter half of the 20th century, LSR revolutionized applications requiring precision molding and enhanced performance characteristics.

LSR’s liquid form and rapid curing at high temperatures opened new possibilities in medical, automotive, and consumer electronics applications. Its biocompatibility and hypoallergenic properties transformed the medical industry by enabling the production of safe, durable, and flexible medical devices and implants.

Properties of Liquid Silicone
Liquid Silicone possesses unique properties that distinguish it from other materials:
High Thermal Stability: It remains stable across a wide temperature range, making it suitable for applications exposed to extreme heat or cold.
Flexibility and Elasticity: LSR maintains its flexibility over time, crucial for products requiring consistent performance under stress or deformation.
Chemical Resistance: It resists degradation from various chemicals, making it ideal for use in harsh chemical environments.
Biocompatibility: LSR is non-toxic and hypoallergenic, posing minimal risk of allergic reactions, making it especially suitable for medical applications.
Electrical Insulation: Its excellent insulating properties make it suitable for electronic and electrical applications.
Chemical Composition
Liquid Silicone (LSR) is composed of a two-part platinum-cured elastomer system. This system utilizes a platinum catalyst to initiate the crosslinking process. The resulting material offers exceptional purity and consistency, as well mechanical properties such as stability, flexibility, and resistance to extreme temperatures and environmental factors.
Solid Silicone also known as High Consistency Rubber (HCR) or conventional silicone rubber, is typically peroxide-cured. In this process, peroxide acts as the catalyst for crosslinking. The resulting material has a firmer and more resilient texture, with slightly different physical and chemical properties compared to LSR.
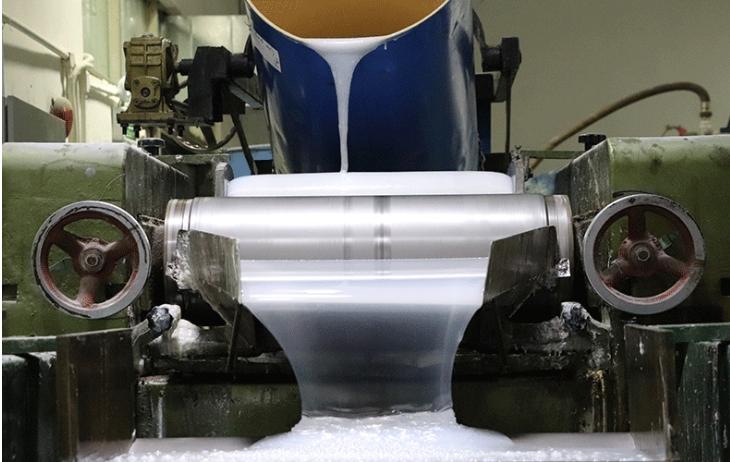

Physical Characteristics
Liquid Silicone (LSR)
Flexibility and Elasticity: Highly flexible and elastic, making it ideal for products requiring a soft touch and repeated motion.
Transparency: Generally more transparent compared to solid silicone.
Low Viscosity: Allows for easy molding and casting into intricate shapes.
Solid Silicone (HCR)
Rigidity and Strength: More rigid and robust, suitable for applications requiring structural integrity.
Opacity: Tends to be more opaque.
Higher Viscosity: Makes it suitable for molding into thicker, more solid forms.
Advantages and Limitation
Advantages of Liquid Silicone (LSR):
Precision Molding: Its low viscosity allows for casting into complex and fine details.
Faster Curing Time: Cures more rapidly than solid silicone, enhancing production efficiency.
High Temperature Resistance: Maintains stability and functionality in extreme temperatures.
Biocompatibility: Particularly advantageous for medical applications.
Limitations of Liquid Silicone (LSR):
Cost: Generally more expensive due to the platinum-curing process.
Equipment Requirements: Requires specialized molding equipment.
Advantages of Solid Silicone (HCR):
Durability: More suitable for heavy-duty applications due to its rigidity and strength.
Cost-Effectiveness: Less expensive compared to LSR.
Limitations of Solid Silicone (HCR):
Design Restrictions: Less flexible for intricate designs due to higher viscosity.
Longer Curing Time: Slower production process.

Manufacturing Process
Injection molding process for liquid silicone (LSR) Products
Preparation and mixing of its two-component system, which typically includes a base silicone and a platinum-based catalyst. The components are kept separate until the molding process begins to prevent premature curing.
Injection molding:Where the two components are thoroughly blended in a dynamic mixer and then injected into a heated mold under high pressure.
Curing:the LSR undergoes rapid curing in the mold, triggered by the heat that activates the platinum catalyst.
Post-Curing and Finishing:After demolding, the parts may undergo post-curing to ensure maximum material properties and any additional finishing as required.

Injection molding process for solid silicone (HCR)
Mixing of silicone rubber base, filler materials, and a peroxide-based curing agent. This mixture is typically processed in a heavy-duty mixer to ensure uniform distribution of all components.
Molding:Solid silicone can be molded using techniques such as compression molding and extrusion. Compression molding involves placing the mixed silicone in a heated mold and applying pressure to shape it, while extrusion involves pushing the silicone through a die to form continuous shapes.
Curing process for solid silicone is slower than for LSR, as the peroxide catalyst reacts during the heating process to create crosslinks between the silicone polymers.
Post-Curing and Finishing: solid silicone parts may undergo post-curing, trimming, inspection, and finishing.
In summary, the manufacturing processes for liquid and solid silicone differ significantly in terms of the materials used, molding techniques, and curing processes. LSR’s injection molding and rapid curing make it suitable for mass production of detailed parts, while solid silicone’s versatility in molding processes lends itself to a wider range of product shapes and sizes.
Environmental Impact
Environmental Impact of Liquid Silicone (LSR):
1. Eco-Friendly Manufacturing:
LSR’s manufacturing process is relatively energy-efficient. The rapid curing time reduces energy consumption during production. Additionally, the precision of injection molding leads to minimal waste, as the amount of material used can be accurately controlled.
2. Durability and Longevity:
LSR products have a long lifespan due to their high durability and resistance to environmental factors like UV light, extreme temperatures, and chemicals. This longevity means fewer replacements and, consequently, less waste over time.
3. Biocompatibility and Safety:
LSR is often used in medical and food-grade products due to its non-toxic nature. It does not leach harmful chemicals, making it a safer choice for both human health and the environment.
4. Recycling Challenges:
While LSR is an environmentally conscious choice in many ways, it presents challenges in recycling due to its thermoset nature, which makes it difficult to remelt and reshape.
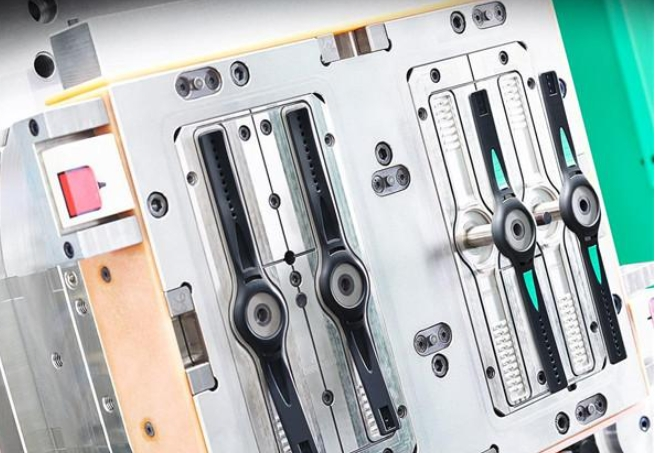

Environmental Impact of Solid Silicone (HCR):
1. Material Efficiency:
Solid silicone rubber, or High Consistency Rubber (HCR), generally has a longer curing time, which can translate to higher energy consumption during production. However, the process often involves fewer volatile organic compounds (VOCs), reducing air pollution.
2. Robustness and Waste Reduction:
The strength and resilience of solid silicone make it suitable for applications where durability is critical. This robustness contributes to less frequent replacements and, therefore, less waste.
3. Recyclability Issues:
Similar to LSR, solid silicone is challenging to recycle due to its thermoset characteristics. While it does not readily break down, its long service life mitigates its environmental impact to some extent.
4. Safe for Various Applications:
Solid silicone is also widely used in cookware, baby products, and medical devices, indicating its safety and non-toxicity, which are important environmental considerations.
Applications in Industry
Medical Devices
– Liquid Silicone (LSR): LSR is commonly used for flexible medical products such as tubing and seals. It is valued for its biocompatibility and resistance to sterilization.
– Solid Silicone (HCR): HCR is employed in sturdier and medical grade items like surgical instrument handles and implants. It is known for its structural integrity and durability.
Automotive Industry
– Liquid Silicone (LSR): LSR is ideal for automotive parts requiring heat resistance, such as gaskets, seals, and hoses. It offers durability under extreme conditions.
– Solid Silicone (HCR): Solid silicone is used for more rigid automotive components like mountings and bushings. It is appreciated for its vibration absorption and weather resistance.
Consumer Goods:
– Liquid Silicone (LSR): LSR or liquid silicon rubber is common in soft and flexible consumer products such as kitchenware and personal care items. It is chosen for its safety and comfort.
– Solid Silicone (HCR): Solid silicone is found in harder consumer products like electronic cases and household tools. It is selected for its longevity and resistance to environmental factors.
In summary, liquid silicone is preferred for applications requiring flexibility and biocompatibility, while solid silicone is better suited for applications needing strength and resilience.
Production Cost Analysis of Liquid Silicone vs. Solid Silicone
Liquid Silicone (LSR) Production Costs:
Material Costs: Liquid Silicone Rubber typically has higher material costs compared to solid silicone due to the use of platinum as a catalyst in its curing process. Platinum-curing is more expensive than the peroxide curing used in solid silicone.
Manufacturing Efficiency: The injection molding process for LSR, although requiring initial investment in specialized machinery, is highly efficient. It allows for rapid production with minimal waste, which can offset some of the higher material costs in high-volume production.
Labor and Energy Costs: The automation potential in LSR molding reduces labor costs. Additionally, the fast curing time of LSR can lead to lower energy costs per unit, contributing to overall cost efficiency in large-scale production.
Solid Silicone (HCR) Production Costs:
Material Costs: The raw materials for solid silicone are generally less expensive than those for liquid silicone. The peroxide curing agents used in solid silicone are more cost-effective than platinum.
Equipment Investment: Manufacturing processes for solid silicone, such as compression molding, often require less expensive equipment compared to the high-precision machinery needed for LSR. This can lower initial setup costs.
Energy and Labor Intensity: The longer curing time for solid silicone can result in higher energy consumption. Additionally, processes like compression molding might require more manual labor, potentially increasing labor costs.

Comparative Analysis:
Volume and Scale: For large-scale productions, the efficiency of LSR can make it more cost-effective despite higher material costs. In contrast, solid silicone may be more economical for smaller-scale or less complex productions.
Complexity of Parts: The complexity and precision of the parts being produced also play a significant role. LSR’s ability to fill complex molds with less waste makes it cost-effective for intricate designs, despite the higher material cost.
By considering these factors, you can make an informed decision on whether to choose liquid silicone or solid silicone based on your specific production requirements and cost considerations.
Durability and Lifespan
Durability Comparison:
LSR is known for its exceptional flexibility and resilience. It maintains its properties under a wide range of temperatures and environmental conditions. It is resistant to degradation from factors such as UV light, ozone, and moisture, which contribute to its overall durability. However, LSR might have limitations in applications where high tensile strength or physical abrasion is a factor.
HCR is characterized by its robustness and ability to withstand physical stresses. It has higher tensile strength, making it more suitable for applications where mechanical wear and tear are prevalent. It also exhibits excellent resistance to environmental factors. However, its less flexible nature might limit its use in applications that require repeated bending or stretching.

Lifespan in Various Applications:
Medical Devices: Both LSR and HCR silicones offer long lifespans in medical applications due to their biocompatibility and resistance to sterilization processes. LSR, being softer, is often chosen for items in direct contact with skin or tissues, while HCR’s strength is advantageous for structural components of medical devices.
Automotive Industry: In the automotive sector, LSR’s heat resistance ensures longevity in engine and electrical system components, while HCR’s physical robustness is ideal for under-the-hood parts that endure mechanical stress.
Consumer Products: For consumer goods like kitchenware and personal care items, LSR’s flexibility and safety make it a long-lasting option. On the other hand, HCR’s durability is beneficial in products like electronic cases and outdoor tools, where wear resistance is key.
In conclusion, both liquid and solid silicone offer considerable durability and lifespan, but their suitability varies depending on the application requirements. LSR excels in environments requiring flexibility and thermal stability, while HCR is better suited for situations demanding high tensile strength and resistance to physical wear.
Safety and Health Considerations
When it comes to the health impacts of liquid silicone (LSR), it is considered ideal for medical applications due to its biocompatibility with body tissues and fluids. LSR is safe for food contact and baby care products as it does not leach harmful substances. Additionally, it is resistant to various sterilization methods, maintaining safety and hygiene.
On the other hand, solid silicone (HCR) is known for its chemical stability, making it safe for a wide range of applications, including direct human contact. It is suitable for cookware as it does not degrade or release harmful substances at high temperatures. Furthermore, HCR has hypoallergenic properties, resulting in a low risk of skin irritation, making it ideal for wearable products like watch straps.
Both liquid and solid silicone offer safety and health benefits, making them suitable for applications where human health is a primary concern. If you are looking for custom silicone baby products, you can consider reaching out to a medical grade silicone products manufacturer that specializes in customization.

Regulatory and Legal Aspects
When it comes to regulatory and legal aspects, silicone products must comply with various regulations to ensure safety and compliance. Legal regulations for silicone products cover health and safety compliance, environmental standards, quality certifications, and compliance with safety standards for specific applications.
For medical and food-grade applications, silicone products must adhere to regulations ensuring they are safe and non-toxic. Medical and food grade silicone products, in particular, need to meet certifications like USP Class VI or ISO 10993 for biocompatibility. Silicone used in food applications must comply with FDA standards for safety in food contact.
In terms of environmental standards, the manufacturing and disposal of silicone products are regulated to minimize their environmental impact. This ensures that the production process and disposal methods are environmentally responsible.
Quality certifications, such as compliance with ISO standards, are often required for silicone products to ensure quality assurance and reliability.
Consumer safety is also an important consideration for silicone products in consumer goods. They are regulated to adhere to safety standards set by organizations such as the Consumer Product Safety Commission (CPSC) in the US.
Conclusion
The future of silicone products looks promising, with ongoing innovations aimed at enhancing their medical applications, sustainability, and technological integration. Regulatory and legal aspects play a crucial role in ensuring the safety, quality, and environmental compliance of these materials.
For those seeking to leverage the benefits of silicone in their products, MoldTechPro offers expert injection molding services. As a leading silicone products manufacturer, we specialize in custom silicone molds, providing tailored solutions to meet your specific needs. Our expertise as a silicone mold manufacturer ensures high-quality, durable, and precise silicone products, aligning with the latest industry standards and innovations.
Whether you require custom silicone mold solutions for medical devices, automotive parts, or consumer goods, MoldTechPro stands ready to deliver excellence in silicone molding, underlining our commitment to quality, innovation, and customer satisfaction in the ever-evolving world of silicone products.
